
Now after some time I came back to the same machine I produced the PR but for some reason I didn't check which branch I was on and made couple of commits on the old branch and pushed them therefore screwing up the PR (it was not yet merged, due to the lack of the test code). I then submitted a PR which was passed the CI build. Just remember to resolve any conflicts that may arise and use other Git commands to manage your repository effectively.I made a local branch in my fork a long time ago and pushed some changes to it. By combining git pull with other Git commands, such as git branch and git push, you can effectively manage your repository and collaborate with others on your project. This helps you to avoid merge conflicts and keep your codebase up-to-date. In conclusion, git pull is an essential command for keeping your repository up-to-date.īy Using git pull regularly ensures that your local repository stays in sync with the latest changes made to the remote repository. Once you have resolved the conflicts, you can commit the changes and complete the merge process by running git commit. You can use a merge tool to help you resolve the conflicts, or edit the files manually. However, If the changes made to the remote and local repositories conflict with each other, Git will stop the merge process and prompt you to resolve the conflicts manually. If there are no conflicts between the changes made to the remote and local repositories, Git performs a fast-forward merge, which updates your local repository with the changes made to the remote repository. Git merges the changes in the origin/ branch with the branch you currently have checked out in your local repository. When you run git merge, Git combines the changes made to the remote repository with your local repository. This allows you to see the changes made to the remote repository without actually merging them with your local repository. Git retrieves the changes made to the remote repository and stores them in a separate branch in your local repository called origin/. When you run git fetch, Git downloads any changes made to the remote repository since the last time you ran git fetch or git pull.

When you run git pull, Git performs two operations: git fetch and git merge. Use git branch to create and manage branches, and use git push to push your changes to the remote repository. By combining git pull with other Git commands such as git branch and git push, you can effectively manage your repository. It’s recommended to use git pull regularly to keep your local repository up-to-date with changes made to the remote repository. Git commit -m "Resolved conflicts" git add You can resolve conflicts by running the following commands: git add To resolve conflicts, Git will prompt you to choose which changes to keep or merge.įor example, if you and your colleague made changes to the same file in the remote and local repositories respectively, Git will prompt you to choose which changes to keep or merge. Thirdly, it’s important to note that git pull can lead to conflicts if there are changes made to the same files in both the remote and local repositories. You can see the changes that were pulled by running the following command: git log -oneline -decorate -graph -all git log -oneline -decorate -graph -all Git will fetch those changes and merge them with your local repository. Visualize Your Git Pull History with Git Log and Graphical Toolsįor instance, if there were changes made to the remote repository since you last pulled the changes.
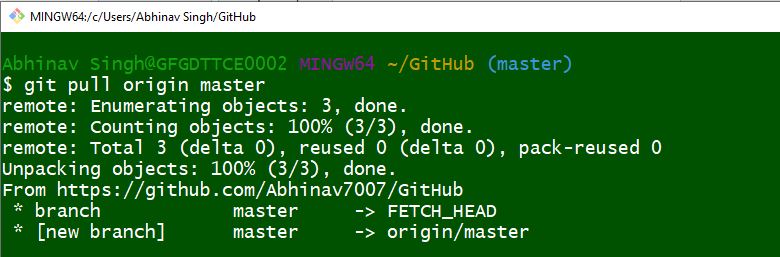
This ensures that your local repository is always up-to-date with the latest changes made to the repository. Secondly, when you run the git pull command, Git will automatically fetch the changes made to the remote repository and merge them with your local repository. You can do so by running the following command: git pull origin git pull origin
#GIT PULL REMOTE BRANCH UPDATES UPDATE#
Then, use git pull to fetch and merge changes from the remote repository to your local one.įor example, let’s say you have a local repository on your computer that you want to update with changes made to the remote repository. If you haven’t created one, run git init.

To use git pull, you need a local repository on your computer. How Does Git Pull Work Behind the Scene?.Visualize Your Git Pull History with Git Log and Graphical Tools.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
